Securely Control Your IoT Devices Remotely: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's interconnected world, the ability to manage and interact with devices from afar is not just a luxury, but a necessity. This is where the power of remote connect IoT device capabilities truly shines, transforming how we monitor, control, and troubleshoot our smart environments, whether at home, in the office, or across vast industrial landscapes.
From smart home appliances to complex industrial sensors and connected vehicles, Internet of Things (IoT) devices are everywhere. Managing such a diverse ecosystem without needing to be physically present at each location offers unparalleled convenience and flexibility, enhancing efficiency and enabling advanced automation. This article will delve into the intricacies of remotely accessing your IoT devices, exploring various methods, best practices, and crucial security considerations to ensure a seamless and safe experience.
Table of Contents
- What is IoT Remote Access and Why is SSH Commonly Used?
- The Unparalleled Benefits of Remote IoT Device Management
- Common Scenarios for IoT Remote Connection
- Navigating the Challenges: Security and Connectivity
- Setting Up Remote Access for Your IoT Devices
- Popular Methods for Remote IoT Device Access
- Risky Practices to Avoid and How to Stay Secure
- Future-Proofing Your IoT Remote Access Strategy
What is IoT Remote Access and Why is SSH Commonly Used?
IoT remote access is fundamentally the capability to connect to, monitor, and control Internet of Things (IoT) devices from a remote location, without needing to be physically present. This crucial functionality allows users to manage and support a wide array of IoT devices, from simple smart plugs in a home to complex industrial machinery in a factory. The convenience and flexibility offered by remote control of devices using IoT are unparalleled, enabling users to monitor, manage, and adjust IoT devices from any location with an internet connection. This enhances efficiency, enables automation, and provides a seamless way to customize and optimize the functioning of connected devices.
Among the various protocols and methods available for remote access, SSH (Secure Shell) is commonly used and highly favored for its robust security features. When you use remote connect IoT device SSH, you are leveraging this secure protocol to interact with your devices safely. SSH ensures that data transmitted between your computer and the IoT device is encrypted, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. This level of security is paramount, especially given the sensitive nature of data often handled by IoT devices and the potential for cyber threats. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network, making it ideal for command-line access, file transfers, and even tunneling other protocols securely.
The Unparalleled Benefits of Remote IoT Device Management
The ability to remotely manage IoT devices brings a multitude of advantages, impacting operational efficiency, cost reduction, and overall business agility. For enterprises, these benefits are particularly significant, driving innovation and competitive advantage in various sectors.
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Savings
Remote access to IoT devices drastically enhances efficiency by allowing administrators to keep a close eye on the performance and status of devices without dispatching personnel. This helps in proactive maintenance, identifying potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. Troubleshooting devices, which traditionally involved sending technicians onsite to connect to those devices, can now often be done remotely. This significantly reduces the complexity and the cost of device management, saving on travel expenses, labor hours, and downtime. Imagine managing hundreds or thousands of devices spread across different geographical locations; remote access makes this feasible and economical.
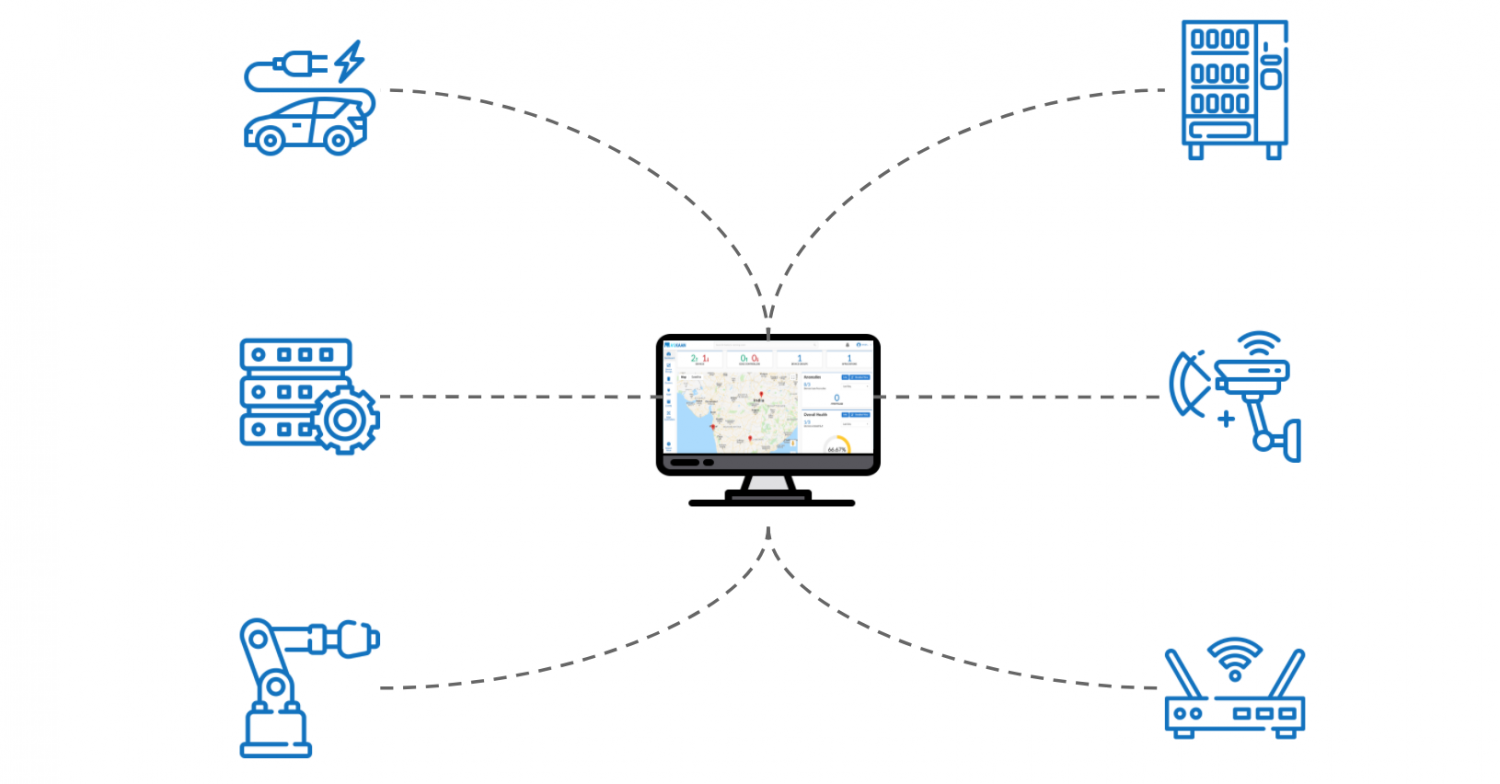
Furthermore, remote monitoring capabilities allow for a complete overview of all your IoT devices in one single dashboard. You can remotely monitor CPU, memory, and network usage, receive alerts based on monitored IoT data, and even run batch jobs on devices. This centralized control and real-time data access enable quicker decision-making and more efficient resource allocation, optimizing device performance and extending their lifespan.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
The deployment of IoT technology is revolutionizing logistics and supply chain management. As per a newly conducted study, the deployment of IoT technology in the global supply chain market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 13.2 percent between the years 2020 to 2030. Remote access to IoT devices plays a pivotal role in this growth. For instance, in logistics, IoT sensors can track the location and condition of goods in transit, and remote access allows for real-time monitoring and intervention if conditions deviate from norms (e.g., temperature fluctuations for perishable goods). This ensures the integrity of the supply chain and provides greater transparency.
The ability to remotely configure and manage IoT devices within a supply chain, from smart warehouses to connected vehicles, enhances operational fluidity. It allows for dynamic adjustments to routes, inventory management, and asset tracking, leading to more resilient and responsive supply chains. This capability directly contributes to reduced waste, improved delivery times, and overall operational excellence.
Common Scenarios for IoT Remote Connection
IoT remote SSH connection is commonly used in three primary scenarios, each addressing a critical need for modern IoT deployments. These scenarios highlight the versatility and necessity of having robust remote access capabilities for your IoT infrastructure.
Remote Monitoring and Management
The most frequent use case for IoT remote access is the continuous monitoring and management of devices. This helps administrators to keep an eye on the performance and status of devices, ensuring they are operating optimally. For instance, in smart cities, sensors monitoring air quality or traffic flow need constant oversight. Remote access allows operators to check data feeds, identify anomalies, and even push software updates or configuration changes without physically visiting each sensor location. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maximizes the efficiency of large-scale IoT deployments.
This also extends to industrial IoT (IIoT) environments where machinery performance, energy consumption, and environmental conditions are critical. Combining remote control functionalities with monitoring capabilities provides a holistic view, enabling predictive maintenance and operational optimization. You can get a complete overview of all your IoT devices in one single dashboard, allowing for quick insights and informed actions.
Troubleshooting and Onsite Support Reduction
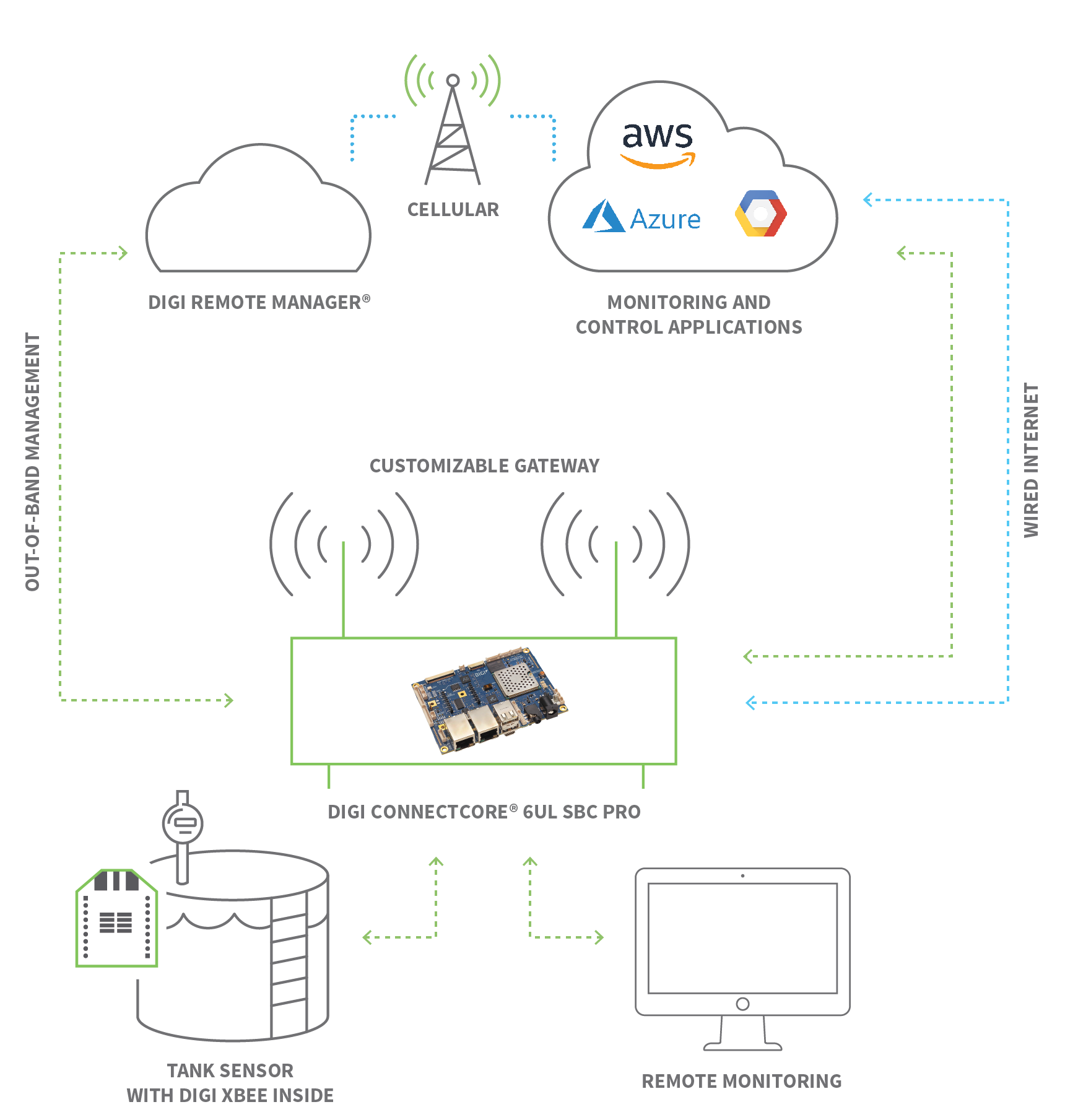
One of the significant challenges with widely distributed IoT devices is troubleshooting. When a device malfunctions or requires a diagnostic check, the traditional approach involves sending technicians onsite. This increases the complexity and the cost of device management. However, with remote access, many troubleshooting steps can be performed virtually. For example, if your device runs a Linux distro (like a Raspberry Pi), you can set up a reverse SSH tunnel, so you can access your device even if it's behind a router or firewall. The thing here is that your device has to start the connection, opening a tunnel to a server, then you can connect to the device through the server.
This capability dramatically reduces the need for physical dispatches, saving time, money, and resources. Technicians can diagnose issues, restart devices, reconfigure settings, or even access logs remotely, resolving problems much faster. This efficiency is particularly valuable for devices deployed at remote sites, behind firewalls that block all inbound traffic, making direct access challenging.
Navigating the Challenges: Security and Connectivity
While the benefits of remote connect IoT device capabilities are immense, deploying and managing them effectively comes with its own set of challenges, particularly concerning security and connectivity. Since IoT devices are often guarded by firewalls and publicly shielded IP addresses, reaching them remotely can be quite challenging.
Using firewalls is a common way to protect and secure access to IoT devices. Yet, it’s challenging to access and manage devices deployed at remote sites, behind firewalls that block all inbound traffic. This necessitates creative solutions like reverse tunnels or cloud-based connectivity services that initiate outbound connections. As a result, some users cut corners to gain remote access to their IoT devices, but in the process, they’re leaving doors open for lurking cybercriminals to sneak in undetected. This underscores the critical importance of secure setup and adherence to best practices.
Connectivity itself can be a hurdle. Ensuring you have a router, modem, or gateway compatible with your IoT device is step one. For industrial environments, robust networking equipment designed for Industrial IoT (IIoT) is essential. Moreover, reliable internet connectivity is paramount. While traditional broadband works for many home setups, large-scale or remote deployments might require alternative solutions. Cellular connectivity is possibly one of the cheapest and most efficient ways to connect IoT devices over the internet, especially for mobile or geographically dispersed devices. Cellular options are more effective since they offer widespread coverage and dedicated IoT plans. Satellite networks can also be used for extremely remote locations where other options are unavailable.
Setting Up Remote Access for Your IoT Devices
Now that we understand the different remote access methods available, let’s move on to the steps involved in setting up remote access for your IoT devices. Setting up remote access for your IoT devices may vary depending on the specific device and manufacturer. However, here are some general steps to guide you through the process.
Prerequisites and Initial Setup
Before you begin setting up your Linux server for remote accessing IoT devices, there are a few prerequisites you need to consider. First, you will need a compatible IoT device and a stable internet connection. Ensure your device is powered on and connected to the network. For home and office environments, this usually means connecting to your Wi-Fi router. For industrial settings, ensure your IIoT devices are connected to robust networking equipment.
Next, you'll need to prepare your remote access server or platform. This could be a dedicated Linux server, a cloud platform account (like AWS IoT), or a service that facilitates remote connections. Ensure your server has a static IP address or a dynamic DNS service configured if it's not cloud-based. You'll also need appropriate login information for your server and, if applicable, for the device manufacturer's cloud platform. Configure your IoT device to connect to the device manufacturer’s cloud platform if that's your chosen remote access route.
Popular Methods for Remote IoT Device Access
There are several established methods for achieving remote connect IoT device functionality, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases. Understanding these options will help you choose the most appropriate solution for your specific needs.
SSH (Secure Shell) Connection
As mentioned, SSH is a cornerstone for secure remote access. It provides a secure channel over an unsecured network by encrypting the traffic between the client and the server. For IoT devices running Linux distributions (like Raspberry Pi), SSH is the go-to for command-line access, file transfers, and secure tunneling. When you use remote connect IoT device SSH Windows, you are leveraging this secure protocol to interact with your devices safely, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. To learn more, refer to how to set up and configure your IoT for remote SSH access over the internet. This method is particularly useful for developers and administrators who need direct, secure command-line control over their devices.
VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
Connect to IoT remotely over the internet using VNC. Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a protocol for safely accessing the IoT graphical user interface (GUI) or desktop. It is widely used for remote device management and file transfer, especially when a visual interface is preferred over a command-line interface. For IoT devices that have a desktop environment (e.g., a Raspberry Pi running a desktop OS), VNC allows you to see and interact with the device's screen as if you were sitting in front of it. This is incredibly useful for graphical applications, debugging visual elements, or training purposes.
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
Similar to VNC but primarily associated with Windows environments, RDP allows users to connect to an IoT device's remote desktop using an RDP client. With XRDP (an open-source RDP server) up and running on your IoT device (if it's Linux-based), you can now connect to it using an RDP client such as Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) in Windows or Remmina in Linux. This provides a full graphical desktop experience, making it easy to manage files, run applications, and configure settings visually, much like VNC but often with better performance over varying network conditions for Windows-based systems or XRDP configured Linux systems.
Cloud Platforms (AWS IoT, Arduino Cloud)
Cloud platforms offer a comprehensive solution for remote connect IoT device management, abstracting much of the underlying networking complexity. How do I use AWS IoT SSH for remote device access? AWS IoT devices require a secure setup with appropriate IAM roles and tunneling, allowing for secure remote access without direct inbound connections to the device. These platforms provide a centralized dashboard to monitor, manage, and interact with devices. The Arduino IoT remote phone application, for example, lets you control and monitor all of your dashboards in the Arduino Cloud. With the app, you can also access your phone's internal sensors such as GPS data, light sensor, IMU, and more (depending on what phone you have). This highlights the power of cloud platforms to integrate device control with mobile applications and other services, offering a highly scalable and flexible remote management solution.
When using cloud platforms, you often select the remote server option under IoT server and supply the IP address of the server, plus the login information. You can then use the remote device to verify the presence of the registered IoT devices. These platforms often handle the complexities of firewalls and dynamic IP addresses through secure tunnels and message brokers, simplifying the remote access process for users.
Risky Practices to Avoid and How to Stay Secure
While the convenience of remote connect IoT device functionality is undeniable, it's crucial to acknowledge and avoid risky IoT remote access practices. Cutting corners to gain remote access to your IoT devices can leave doors open for lurking cybercriminals to sneak in undetected. Security should always be a top priority when dealing with remotely accessible devices.
One common risky practice is using default passwords or weak credentials. Always change default passwords immediately and use strong, unique passwords for all your IoT devices and remote access services. Another risk is exposing devices directly to the internet without proper firewall rules or security layers. Never forward ports directly to an IoT device unless absolutely necessary and with extreme caution. Instead, utilize secure tunneling solutions (like reverse SSH tunnels) or cloud-based IoT platforms that manage secure connections.
Regularly updating your device firmware and software is also critical. Manufacturers often release updates that patch security vulnerabilities. Neglecting these updates leaves your devices exposed. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible for remote access logins. Finally, continuously monitor your device activity for any unusual patterns that might indicate a breach. By adhering to these security principles, you can significantly mitigate the risks associated with remote IoT access.
Future-Proofing Your IoT Remote Access Strategy
As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, so too must your strategies for remote device management. Future-proofing your approach involves embracing scalable solutions, staying abreast of emerging security threats, and leveraging advanced analytics to gain deeper insights into device performance and security posture. The ability to remote connect IoT device is not static; it's a dynamic field requiring continuous adaptation.
Consider adopting a unified dashboard approach that combines remote control functionalities with monitoring capabilities. This allows you to get a complete overview of all your IoT devices in one single dashboard, enabling proactive management and rapid response to issues. Look for solutions that offer robust alerting mechanisms based on monitored IoT data, allowing you to receive notifications for critical events like CPU, memory, or network usage spikes, or unexpected device disconnections. Furthermore, the ability to run batch jobs on devices remotely will become increasingly important for managing large fleets efficiently, pushing updates, or executing diagnostics across multiple devices simultaneously.
Investing in networking equipment designed for industrial IoT (IIoT) is crucial for industrial environments, ensuring reliability and robustness. Exploring cellular or satellite connectivity options for remote or mobile deployments can also future-proof your network infrastructure. Ultimately, a secure, scalable, and intelligent remote access strategy will be key to unlocking the full potential of your IoT deployments for years to come.
In conclusion, mastering how to remote connect IoT device is essential for anyone looking to leverage the full potential of their smart infrastructure. From enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs to enabling advanced troubleshooting and logistics optimization, the benefits are clear. While challenges like security and connectivity exist, by adopting secure practices, utilizing robust protocols like SSH, VNC, and RDP, and leveraging powerful cloud platforms, you can ensure your IoT devices are accessible, manageable, and secure from anywhere in the world. Embrace these strategies to build a resilient and efficient IoT ecosystem.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the world of remote IoT device management. What are your experiences with remotely connecting to IoT devices? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!

Mastering Remote Access To IoT Devices With SSH: A Comprehensive Guide
Use RemoteIoT Web-Based SSH To Remotely Access IoT Devices Server
RemoteIoT Device Connect Software Download: A Comprehensive Guide