Unlock Your Pi: Free Raspberry Pi Remote Access From Anywhere
In today's interconnected world, the ability to control devices remotely has become not just a convenience, but often a necessity. For enthusiasts and professionals alike, mastering Raspberry Pi remote access free solutions can transform how you interact with your microcomputers, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. Whether you're managing a single project at home or overseeing a "fleet" of remote microcomputers deployed across various locations, knowing how to securely and freely access your Raspberry Pi from afar is an invaluable skill. This article will guide you through several easy and effective methods to achieve just that, ensuring your projects remain accessible, no matter where you are.
The demand for secure and efficient methods to manage IoT devices remotely continues to rise. Gone are the days when you needed a dedicated monitor, keyboard, and mouse tethered to each Raspberry Pi. Modern solutions allow you to connect to your Raspberry Pi desktop and command line directly from any browser or device, making remote access to your Raspberry Pi not only possible but incredibly convenient. Let's explore the best free options available, from the latest offerings by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to time-tested protocols like SSH and VNC.
Table of Contents
- Why Remote Access Your Raspberry Pi?
- Understanding Raspberry Pi Remote Access Fundamentals
- Raspberry Pi Connect: The Foundation's Free Solution
- SSH: Your Command-Line Gateway to Raspberry Pi Remote Access
- VNC and Other Desktop Sharing Solutions
- Chrome Remote Desktop: Google's Free & Official Offering
- Navigating Network Challenges: Firewalls, NAT, and Mobile Data
- Best Practices for Secure Raspberry Pi Remote Access
Why Remote Access Your Raspberry Pi?
The primary motivation behind seeking Raspberry Pi remote access free solutions often boils down to convenience and practicality. Imagine you've set up your Raspberry Pi as a home automation hub, a media server, or a security camera system. What happens if you need to make a quick adjustment while you're at work, or troubleshoot an issue when you're visiting a friend's house? Without remote access, you'd be forced to physically return to your Pi's location, connect a monitor, keyboard, and mouse, and then perform your tasks. This is not only cumbersome but also inefficient. Eliminating the keyboard, mouse, and monitor can save you money and space, especially when you consider the cost and clutter of peripherals for multiple devices. This setup is particularly useful for managing your Raspberry Pi without needing a dedicated monitor, keyboard, or mouse connected to it. Furthermore, for those who maintain a "fleet" of remote microcomputers – perhaps for environmental monitoring, distributed computing, or IoT sensor networks – remote access becomes absolutely critical. It allows for centralized management, pushing updates, running diagnostics, and accessing your Raspberry Pi projects from anywhere, ensuring operational continuity and reducing the need for costly on-site visits.The Growing Need for IoT Device Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding at an exponential rate, with Raspberry Pi devices frequently serving as the backbone for countless IoT applications. From smart home devices to industrial sensors, these microcomputers are often deployed in environments where direct physical access is impractical or impossible. The demand for secure and efficient methods to manage IoT devices remotely continues to rise, driven by the need for scalability, reliability, and security. For instance, consider a scenario where you have several Raspberry Pis monitoring temperatures in different rooms of a large building. If one sensor goes offline or requires a software update, remote access allows you to diagnose and rectify the issue without physically visiting each location. This capability is not just about convenience; it's about enabling new possibilities for automation, data collection, and system maintenance in a world increasingly reliant on distributed computing. The idea is to control your Raspberry Pi from another computer, either on the same local network or from anywhere (depending on the solution you use), making it a truly versatile IoT device.Understanding Raspberry Pi Remote Access Fundamentals
Raspberry Pi remote connect refers to the ability to access and control your Raspberry Pi device from another computer or device over a network. At its core, remote access means interacting with your Pi as if you were sitting directly in front of it, even if you're miles away. This interaction can range from executing simple command-line instructions to full graphical desktop control, depending on the method chosen. The fundamental concept revolves around establishing a secure communication channel between your client device (e.g., your laptop, smartphone, or another computer) and your Raspberry Pi. This channel can be established over a local area network (LAN), where both devices are connected to the same router, or over the internet, allowing access from anywhere in the world. While local network access is often straightforward, accessing your Raspberry Pi from work or a friend's house introduces complexities like firewalls and network address translation (NAT) routers, which we'll address later. The goal is always to achieve a direct connection to Raspberry Pi behind a firewall from anywhere, as if it was on the local network.Common Remote Access Protocols
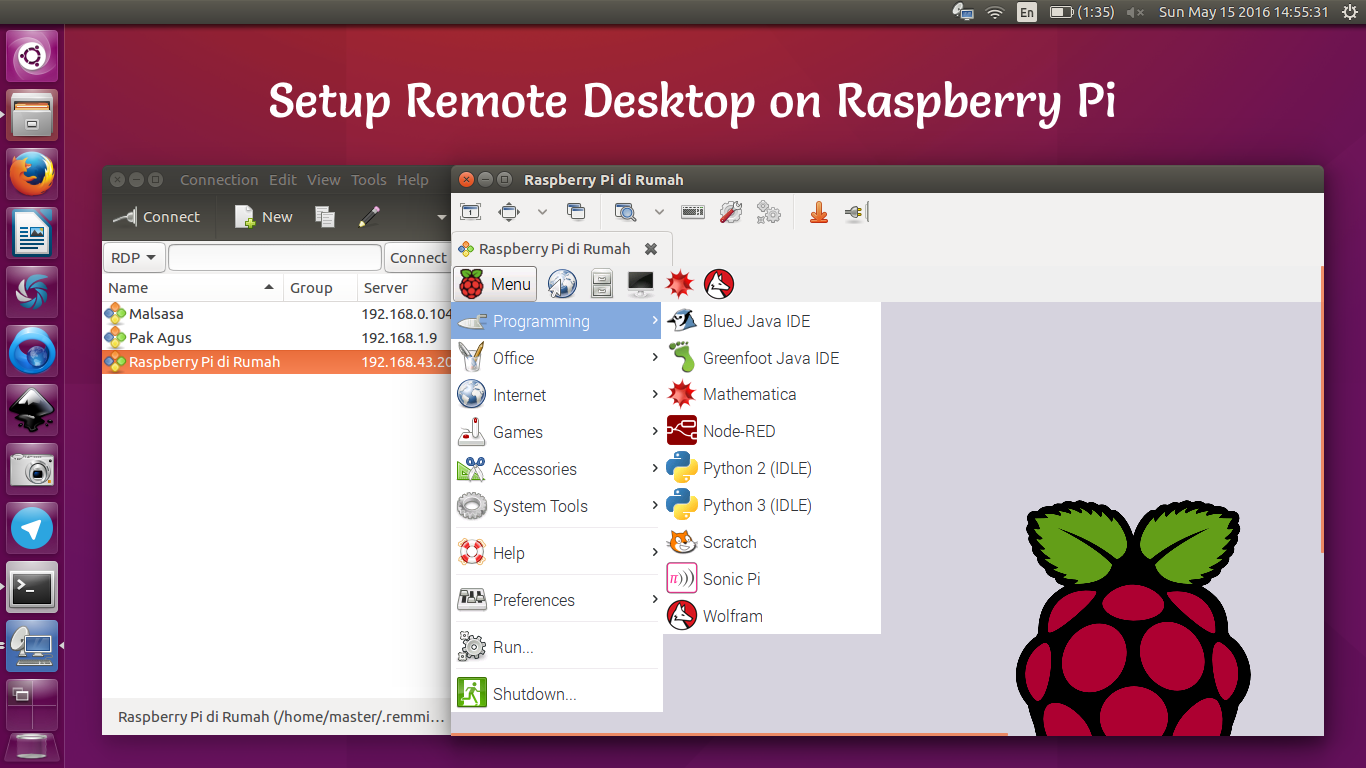
Several protocols and software solutions facilitate remote access, each with its own strengths and ideal use cases. Understanding these common methods is crucial for choosing the best Raspberry Pi remote access free option for your specific project: * **SSH (Secure Shell):** This is the most fundamental and widely used method for remote terminal access. SSH provides a secure, encrypted connection to your Raspberry Pi's command line. It's lightweight, efficient, and perfect for managing your Pi without a graphical interface, such as running scripts, installing software, or checking system status. With the best SSH remote IoT device Raspberry Pi free options, you can remotely control your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world. * **VNC (Virtual Network Computing):** VNC allows you to view and control your Raspberry Pi's graphical desktop environment remotely. It's like having a virtual monitor connected to your Pi, enabling you to use applications, browse the web, or interact with the desktop just as you would locally. Solutions like VNC can provide remote access to a Raspberry Pi over the internet. * **RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol):** While more commonly associated with Windows, XRDP is an open-source implementation that allows Linux systems, including Raspberry Pi OS, to accept RDP connections. Similar to VNC, it provides a graphical desktop experience. * **Web-based Solutions:** Newer solutions, including the Raspberry Pi Foundation's own offering, provide browser-based access, often simplifying the setup process by abstracting away network complexities. These can allow you to send commands and batch jobs to Raspberry Pi from a web portal. Each of these methods offers a unique way to interact with your Raspberry Pi, providing flexibility depending on whether you need a command-line interface or a full graphical desktop experience.Raspberry Pi Connect: The Foundation's Free Solution
Today, the Raspberry Pi Foundation is releasing a new solution to simplify and secure access to a remote Raspberry Pi. They have just announced a new way to remotely access a Raspberry Pi, and it's a game-changer for many users. Raspberry Pi Connect is a free screen sharing and remote shell service provided by Raspberry Pi, offering a seamless and secure remote access solution for Raspberry Pi OS. This innovative service allows you to connect to your Raspberry Pi desktop and command line directly from any browser, making it incredibly convenient to access your Raspberry Pi projects from anywhere. The beta release of Raspberry Pi Connect marks a significant step forward in simplifying remote access. One of its most compelling features is its ability to bypass complex network configurations. There's no need to discover the IoT device IP and change any firewall settings. Now, you can access your Raspberry Pi from anywhere, as if it were on your local network, even if it's behind a firewall or NAT router. This eliminates the headache of wrestling with complex firewall configurations or memorizing dynamic IP addresses, a common hurdle for many remote access setups. To use Raspberry Pi Connect, you typically sign in with your Raspberry Pi account. The service handles the underlying network complexities, creating a secure tunnel that allows your browser to communicate directly with your Pi. This means you can use Raspberry Pi Connect, a free screen sharing and remote shell service, to manage your device whether you're at home, work, or on the go. If you’re interested in Raspberry Pi Connect, you’ll also want to read our more recent update, about remote shell access and support for older Raspberry Pi devices, as the Foundation continues to refine and expand its capabilities. This solution truly embodies the spirit of accessible computing, offering a robust and free method for Raspberry Pi remote access free.SSH: Your Command-Line Gateway to Raspberry Pi Remote Access
Secure Shell (SSH) is arguably the most fundamental and widely used method for remote access to your Raspberry Pi's command line. It provides a secure, encrypted channel over which you can execute commands, transfer files, and manage your Pi without a graphical interface. For many users, SSH is the go-to solution for its simplicity, efficiency, and robust security features. With the best SSH remote IoT device Raspberry Pi free options, you can remotely control your Raspberry Pi from anywhere in the world, making it an indispensable tool for headless setups. To enable SSH on your Raspberry Pi, the process is straightforward: 1. **Boot your Raspberry Pi** and connect it to a monitor, keyboard, and mouse for initial setup (or use `raspi-config` via a local terminal if you're already connected). 2. **Open the Raspberry Pi Configuration menu.** You can find this under "Preferences" in the main menu, or by typing `sudo raspi-config` in the terminal. 3. **Navigate to "Interface Options"** (or "Interfacing Options" in older versions). 4. **Select "SSH"** and then choose "Yes" to enable it. 5. **Reboot your Pi** for the changes to take effect. This single option is all you need to start SSH automatically on every boot. Once enabled, you can connect from another computer on the same network using an SSH client (like PuTTY on Windows, or the built-in terminal on Linux/macOS). You'll need to find the IP address of your Raspberry Pi, which you can do by typing `hostname -I` in the Pi's terminal. Then, from your client device, simply type `ssh pi@your_pi_ip_address` (replacing `your_pi_ip_address` with the actual IP).Automating SSH Access on Boot
To make remote access more convenient, we can configure the SSH server to start automatically whenever your Pi boots up. As mentioned, enabling SSH through the Raspberry Pi Configuration menu (under Interfaces) automatically sets it to start on boot. This ensures that your Pi is always ready to accept SSH connections without manual intervention after a power cycle or reboot. For advanced users, you can also manage SSH services directly using systemd commands: * `sudo systemctl enable ssh` to ensure it starts on boot. * `sudo systemctl start ssh` to start the service immediately. * `sudo systemctl status ssh` to check its current status. Automating SSH access is particularly useful for headless setups where you don't have a monitor connected. It means that once your Pi is powered on and connected to the network, you can immediately access it via SSH from any device on the same network, or even from outside your local network if you configure port forwarding or a tunneling service. This foundational method is a cornerstone of Raspberry Pi remote access free, providing robust command-line control.VNC and Other Desktop Sharing Solutions
While SSH provides powerful command-line access, sometimes you need to access a Raspberry Pi with a graphical interface, especially if you're working on projects that require visual interaction or specific desktop applications. This is where Virtual Network Computing (VNC) comes into play. VNC allows you to view and control your Raspberry Pi's desktop environment remotely, providing a visual "window" into your Pi's graphical user interface. To set up VNC on your Raspberry Pi: 1. **Ensure you have a desktop environment installed** (Raspberry Pi OS Full comes with one by default). 2. **Install a VNC server** (e.g., RealVNC Server, which is often pre-installed or easily installable via `sudo apt install realvnc-vnc-server`). 3. **Enable VNC** through the Raspberry Pi Configuration menu, similar to how you enabled SSH. 4. **Install a VNC client** on your client device (laptop, phone). RealVNC Viewer is a popular choice and is available for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. 5. **Connect using your Pi's IP address** and the VNC password you set during configuration. Solutions like VNC, or XRDP (another remote desktop protocol, commonly used with Windows Remote Desktop Connection clients), can provide remote access to a Raspberry Pi over the internet, though they often require port forwarding on your router for external access, which can introduce security considerations. Beyond VNC and XRDP, other third-party solutions exist. For example, TeamViewer, while not strictly free for commercial use, offers a robust remote access solution that can also be configured on a Raspberry Pi. These solutions often simplify connection over the internet by handling firewall traversal automatically, making them appealing for users who prefer not to delve into network configurations. However, for truly Raspberry Pi remote access free solutions that offer desktop control, VNC remains a strong contender.Chrome Remote Desktop: Google's Free & Official Offering
Chrome Remote Desktop (CRD) by Google is another excellent, free, and officially supported remote access solution for the Raspberry Pi. What makes CRD particularly appealing is its ease of use and cross-platform compatibility. It offers native apps for Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, and Android, meaning you can access your Raspberry Pi from virtually any device with a Chrome browser or the dedicated mobile app. This broad support makes it an incredibly versatile option for anyone seeking Raspberry Pi remote access free. The setup process for Chrome Remote Desktop is remarkably simple. After installing the Chrome Remote Desktop package on your Pi, you simply log into a Google account on any Chrome browser or mobile app. This ties your Pi to your Google account, allowing for seamless authentication and connection without needing to remember IP addresses or configure complex network settings. It leverages Google's infrastructure to establish a secure, encrypted connection, often bypassing firewall issues that plague traditional direct connections.Setting Up Chrome Remote Desktop
Here’s a simplified overview of how to set up Chrome Remote Desktop on your Raspberry Pi: 1. **Install Chrome Remote Desktop on your Raspberry Pi:** This usually involves downloading and installing a specific `.deb` package from the Chrome Remote Desktop website or Google's official documentation for Linux systems. 2. **Install the Chrome Remote Desktop extension** on the Chrome browser you'll use to access your Pi. 3. **Authorize your Pi:** Follow the on-screen prompts to authorize your Pi to be remotely accessed via your Google account. You'll typically generate an authorization code on your Pi and enter it into your Chrome browser on your client device. 4. **Set a PIN:** Create a secure PIN that you'll use to authenticate connections to your Pi. 5. **Connect:** From any Chrome browser or the Chrome Remote Desktop mobile app, log into the same Google account. Your Raspberry Pi should appear in the list of available devices, ready for connection. This method is particularly user-friendly for those who are already integrated into the Google ecosystem. It provides a full graphical desktop experience, allowing you to control your Raspberry Pi device from a different computer or mobile device as if you were sitting directly in front of it. It's a robust and reliable choice for casual users and those who prefer a straightforward setup without deep dives into network configurations.Navigating Network Challenges: Firewalls, NAT, and Mobile Data
Accessing your Raspberry Pi from the same local network is often straightforward. However, the real challenge arises when you want to connect from outside your home network – from work, a friend's house, or even using mobile data. This involves navigating network complexities like firewalls and Network Address Translation (NAT) routers. Remotely accessing Raspberry Pi behind a firewall or NAT router requires specific configurations to allow incoming connections. Traditional methods for external access often involve: * **Port Forwarding:** Configuring your home router to direct specific incoming network traffic (e.g., SSH on port 22, VNC on port 5900) to your Raspberry Pi's internal IP address. This requires knowing your router's interface and often your public IP address (which can change). * **Dynamic DNS (DDNS):** Since most home internet connections have dynamic public IP addresses (meaning they change periodically), DDNS services map a static hostname (e.g., `myrpi.ddns.net`) to your dynamic IP, so you don't have to constantly find the IP address of your Raspberry Pi. While effective, these methods can be daunting for beginners and may raise security concerns if not configured carefully. This is where modern tunneling services and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) shine. Services like remote.it simplify the process immensely. With remote.it, managing multiple Raspberry Pi devices remotely becomes incredibly simple. There's no need to wrestle with complex firewall configurations or memorize dynamic IP addresses. These services create a secure tunnel from your Pi to their servers, allowing you to connect to your Pi via their platform, effectively bypassing NAT and firewalls. This means you can directly connect to Raspberry Pi behind a firewall from anywhere as if it was on the local network. Furthermore, a common question is: "Can I use mobile data to access my Raspberry Pi?" Yes, you absolutely can! Ensure that your client device (laptop, phone, etc.) is connected to the internet through mobile data and that you have configured one of the remote access methods (port forwarding/DDNS, tunneling service, or VPN). Solutions like Raspberry Pi Connect, Chrome Remote Desktop, or tunneling services like remote.it are particularly well-suited for mobile data access, as they handle the underlying network routing without requiring direct IP connections or complex router setups. This flexibility ensures that your Raspberry Pi remote access free is truly available from anywhere, on any network.Best Practices for Secure Raspberry Pi Remote Access
While the convenience of Raspberry Pi remote access free is undeniable, security should always be a top priority. As you open your Pi to external connections, you also open potential avenues for unauthorized access. Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect your data and your device. Here are essential best practices to ensure your remote access setup is secure: 1. **Change Default Credentials:** The default username for Raspberry Pi OS is `pi`, and the default password is `raspberry`. These are widely known. Immediately change the password for the `pi` user, or even better, create a new user with administrative privileges and disable
How to Access Your Raspberry Pi Remotely (Mac/Windows/Linux)
Free Remote Raspberry Pi Management Platform: Your Ultimate Guide

How To Set Up Raspberry Pi Remote Access Over Internet Free A Complete